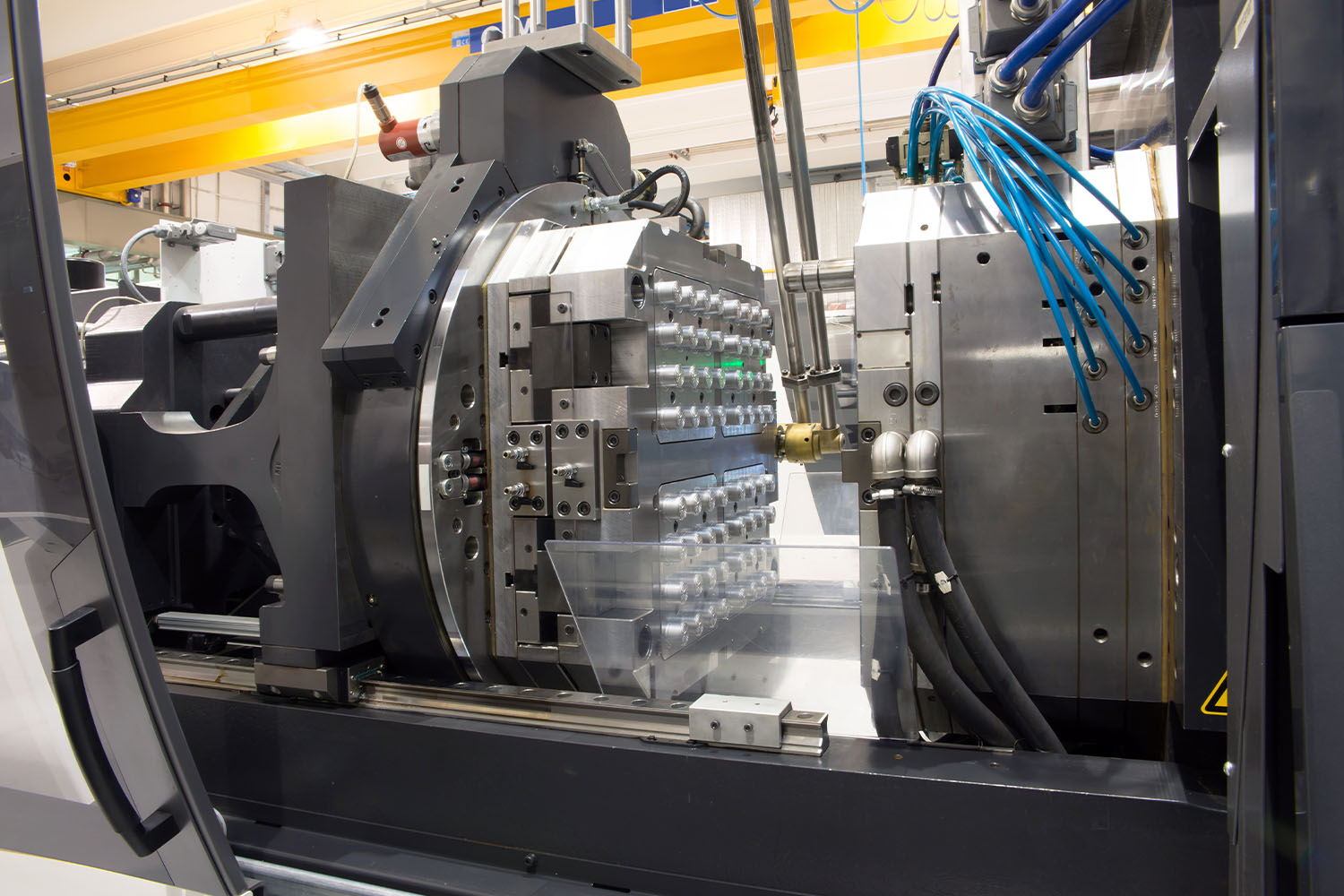
Plastic Injection Molding Machines
Choosing the best manufacturing process, such as injection molding machines, profile extrusion, or thermoforming for your plastics project can seem overwhelming. You need to consider the types of material you need, the price point you aim to hit, the size of your run, and what you want the finished product to look like. On top of that, you must ensure that you can get your parts and products delivered in the time frame you need them.
Manufacturing has been slowly moving overseas in an attempt to lower costs. But the fact is, expensive shipping costs, longer wait times, and inconsistent quality can end up causing your plastic part or product to cost more than you initially thought.
CBM Plastics knows the problems that companies face with their plastics manufacturing. As an automotive plastic parts manufacturer, they have the experience and know-how to solve these problems, providing their customers with quality plastic parts or products when they need them and at a price that still allows them to turn a profit. CBM Plastics is U.S.-based, meaning less inconsistency and uncertainty with shipping and a better ability to control the quality of your part or product.
Want to learn more about CBM Plastics’ manufacturing capabilities? Read on to learn how our injection molding machines work, or contact us today to discuss your project.
What Does a Plastic Injection Molding Machine Do?
A plastic injection molding machine is a manufacturing machine designed to turn plastic polymers and resins into plastic parts and products. The injection molding process will essentially heat plastic material to its melting point, and the injection unit will force it into a created mold. Once in the mold, the part or product will harden as it cools, and the solid product will be ejected.
How Does a Plastic Molding Injection Machine Work?
An injection molder works through a simple four-step process that turns your chosen plastic material into the desired hardened plastic shape.
Step 1
The injection molding machine will have a feeder or hopper where the plastic pellets or granules are introduced. The feeder is cylindrical, heated, and sits on the top of the machine. The material will feed into the hopper or feeder when the injection screw is turned. The material will be heated along the way to a temperature that will turn it into a liquid form.
Step 2
Once the plastic material is melted and reaches the end of the barrel, the gate will close. This allows only a certain amount of plastic to enter the mold. The two parts of the mold will then close together and stay together under clamping pressure as the melted plastic enters the mold cavity. The molten material will not enter the mold until the appropriate pressure is reached to prevent plastic from escaping.
Step 3
The third step of the process includes the time period that the melted plastic will sit in the mold. This is often referred to as the holding time and can be as short as milliseconds to as high as a few minutes. The time needed will depend on the properties of the thermoplastic material and how complex the mold is.
Once the holding time has been completed, the screws will pull back, releasing the pressure and allowing the plastic to cool down and harden. Cooling time will also vary based on the type of plastic and thickness and can be as short as a few seconds to as high as several minutes.
Step 4
Once the plastic in the mold has cooled, a set of plates or pins will eject the part out of the tooling. The part will be ejected onto a conveyor belt or a compartment unless other finishing processes, such as polishing, are required. After this process is done, the product or part will be ready for assembly or packaging.
What Are the Basic Types of Plastic Injection Molding Machines?
There are three primary machine types for plastic injection molding: hydraulic, electric, and hybrid. The type of machine used will depend on the chosen power source that is desired.
Hydraulic
Hydraulic injection molding machines were the first option for injection molding until the electric models came out in the 80s. Many companies still use hydraulic machines for many reasons. They can cost significantly less than other models, have cheaper parts, and are made from more durable components, which makes them last longer. Hydraulic machines also have a higher clamping force than other options.
Electric
When all-electric injection molding machines first became available in the 1980s, they quickly rose in popularity for several reasons. They are considered more energy-efficient as they only consume energy when used. Since they don’t require oil or filters, they have less downtime for maintenance. Electric machines are also known to be faster and easier to operate as they are digitally controlled.
Hybrid
Hybrid plastic injection machines can offer greater diversity by pairing the energy efficiency and energy savings of an electric machine with the clamping force of a hydraulic one. While these machines require oil, they use a fixed-speed DC pump motor with variable-speed AC, allowing it only to use the oil it needs to complete the process.
How Does an Injection Molding Machine Regulate the Amount of Plastic Injected?
To ensure that a mold is not overfilled and no plastic is wasted, the injection molding machine will regulate the amount of molten plastic that enters the cavity. Once the material is in the hopper, it will feed through a check valve and accumulate at the front of the injection screw.
The volume this area holds is also referred to as a shot and will be the amount of liquid plastic needed to fill the mold cavity properly. This amount will compensate for shrinkage and the amount of material that will not fully expel from the barrel keeping the screw from bottoming out. Once the proper volume is reached, the material will be forced into the cavity, where the holding and cooling process will begin.
What Materials Are Used for Injection Molding Machines?
One of the benefits of plastic injection molding is that it can utilize a wide range of plastic polymers, which allows you to choose materials with the properties and features you need for your final part or product. Some of the most commonly used plastics for a variety of industries and products include:
- ABS: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene has a lower melting point, making it easier to mold. It also works well with colorants, allowing you to better customize the look of your final product. The polymer is impact resistant and strong. It is commonly used in automotive body parts, electric outlets, and protective gear.
- PC: Polycarbonate is lightweight and transparent, making it ideal when creating parts or products that need to support light transmission. It is a popular option for clear tubing, machine guards, and tinted windows. The material is durable and heat resistant.
- PE: Polyethylene is one of the most commonly used plastics in many applications and products. It is chemical resistant, flexible, and a good option for many indoor applications. This type of material is often utilized in products such as toys and food containers.
- POM: Polyoxymethylene is rigid and thermally stable, making it ideal for producing firearms, frames, knife parts, and system locks. Its stiffness and strength can also be improved when reinforced with fiberglass.
- PP: Polypropylene is another widely used plastic in manufacturing throughout the world. It has a high chemical resistance, is good at returning to its shape, and is recyclable. Polypropylene is found in storage containers, packages, appliances, and sporting goods.
- PS: Polystyrene is lightweight, inexpensive, and resists bacteria and moisture. This type of polymer is most commonly found in medical supplies and equipment, optical parts, and electronics.
- TPE: Thermoplastic elastomer blends plastic and rubber to combine the properties of both. It is extremely flexible and easy and less expensive to mold. This material is often found in pet products, footwear, and automotive parts.
TPU: Thermoplastic polyurethane Is another popular rubber-like plastic known for its elasticity and resistance to chemicals and extreme temperatures. It is used to produce gaskets, closures, sporting goods, and enclosures for medical devices.
What Are the Benefits of Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic processing using an injection press has several benefits over other forms of plastic manufacturing. Many businesses choose plastic injection molding in Illinois for their production needs because:
It Can Use a Wide Range of Materials and Colors
Plastic injection molding machines can provide a lot of variety when it comes to material usage, colors, and finishes. This will allow you to find a material with the properties that you need your product or part to have and also the final design look that you desire.
It Can Allow You To Use More Complicated Designs
The plastic injection process is a high-precision process that allows for tight tolerances. This will enable you to manufacture more intricate designs and have consistent results even on long or repeat runs.
It Is Extremely Efficient
The automation that comes with injection molding and the high speed of the molding process allows for a more energy-efficient manufacturing process. The time it takes to mold a part or product takes around 2 minutes or less, even with more complex designs. This allows you to output a significant amount of product in a short period of time.
It Offers Better Consistency
Since the mold will set the design, size, and thickness of your product and the injection screws control the amount of molten material feeding into the mold, you will enjoy better consistency and quality control through even large volume runs.
It Produces Little Waste
There is little waste when you use injection molding. Any scrap plastic that needs to be removed after the mold can easily be remelted and reinjected, creating minimal waste.
It Is a Low-Cost Option
When running high volumes of plastic parts or products, injection molding is one of the most cost-effective options. While initial tooling costs can be high, the mold can be used for long runs or multiple runs before it wears out. Since the process is quick and automated, you will enjoy a low per-piece price for large runs.
Do You Have Questions About Plastic Molding Machines? Contact CBM Plastics Today
The experienced professionals at CBM know the ins and outs of molding injection machines and plastic products and are waiting to find the right solution for your plastic project. CBM focuses on high quality, short lead times, and solid delivery dates so that their customers can depend on them no matter the size or scope of the project. Want to learn more about plastic molding machines or plastics manufacturing? CBM is waiting for your call. Contact one of our specialists today to discuss your project needs.
Curious About How Plastic Injection Molding Machines Are Evolving? Want to Discover the Latest Custom Solutions?
Dive into our new article to explore the recent innovations in custom plastic injection molding. Uncover how these breakthroughs are revolutionizing the industry, offering unparalleled precision and creativity in manufacturing. Don’t miss out on learning how these advancements can benefit your projects. Check out our Custom Plastic Injection Molding FAQs to get answers to common questions and gain deeper insights. Read now for a glimpse into the future of plastic molding!

